|
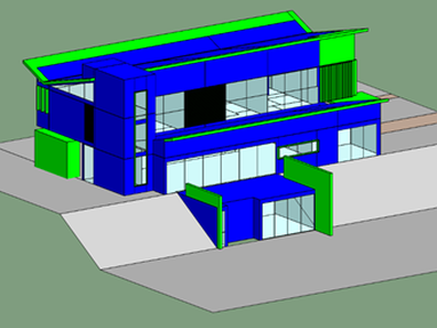
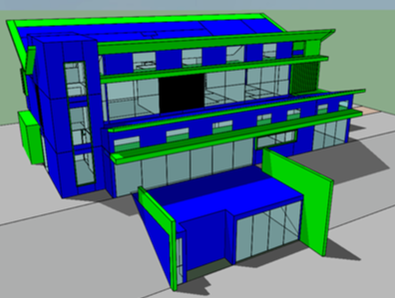
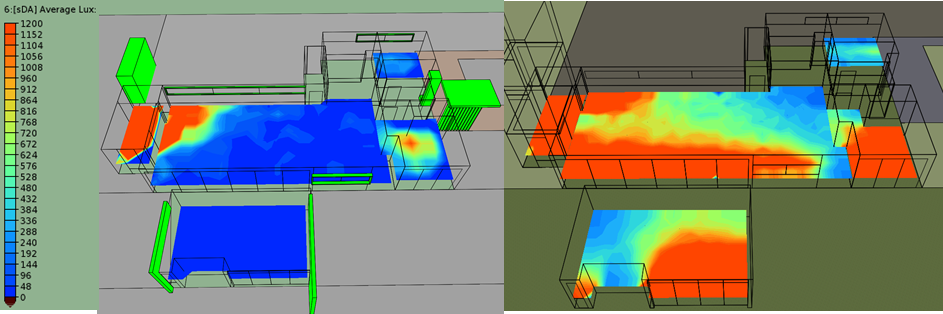
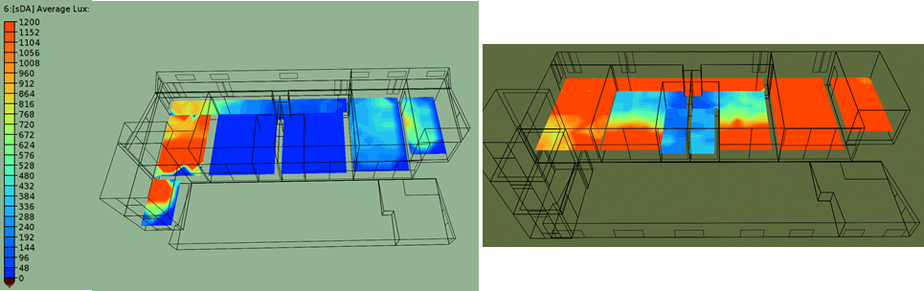
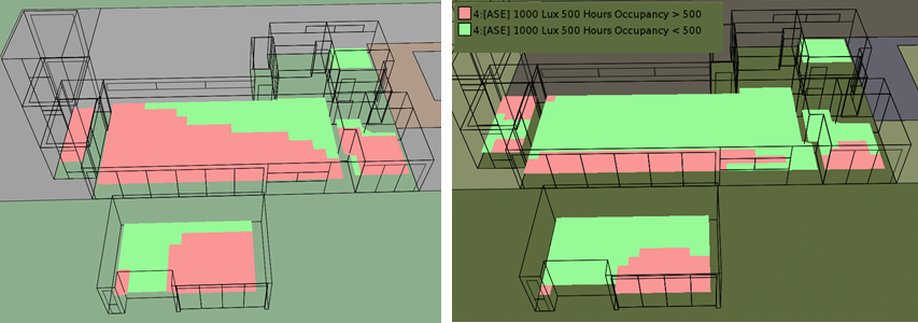
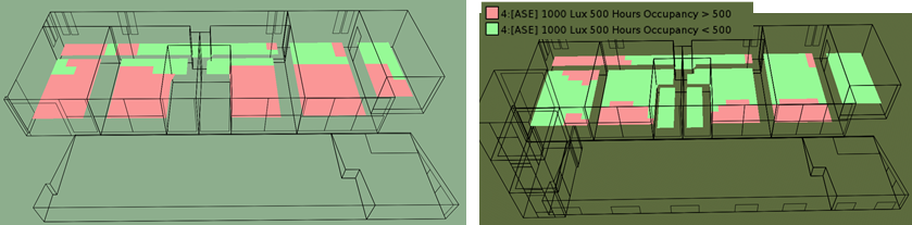
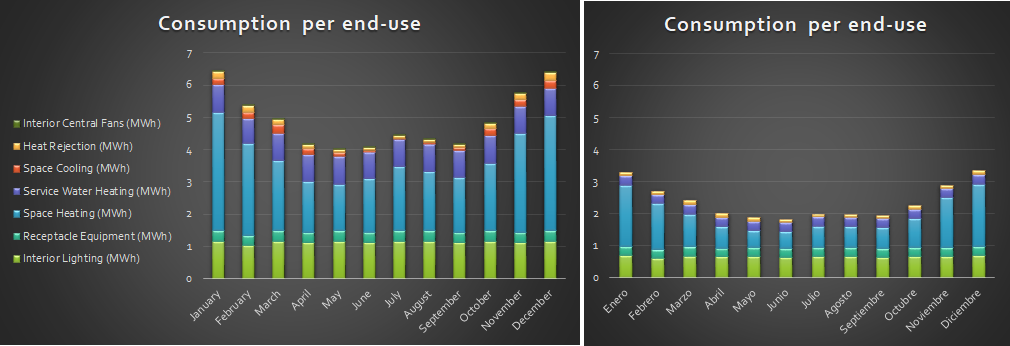
The architecture industry is evolving to be more integrated and focusing on reduced energy consumption and increasing occupant comfort. Our team has worked closely with OWN*, Environment Friendly Mexican Architecture firm, to improve their latest single-family project at conceptual design phase. Our objectives were to reach Net-Zero Energy, maximize daylight while minimizing glare and take advantage of natural ventilation for passive cooling. We perform analysis using a building energy model and CFD simulations. The site climate requires to reduce heating consumption in particular during the night and reduce cooling consumption at mid-day. The temperature is reaching lower temperatures in January, but it is quite constant through the year since the project is located in the north tropical region. We thus would need to reduce slightly solar gain at summer when the sun is at its zenith, this was achieved by adding light shelves that are required to minimize glaring and increase daylight penetration. The light shelves location to not interfere with glass door operation were placed above them, thus additional glazing was placed above the lights shelves. The additional glazing would also contribute, those openable, to increase the natural ventilation potential. However, the light shelves were not enough to reduce the glare enough, thus a glazing film that reduces the visual light transmittance to 17% in strategic locations. These strategies allow the increase in daylight from 34% sDA** to 76% sDA and reduce glare from 72% ASE*** to 25%ASE, all numbers are the weighted average for the occupied spaces. To study the heating/cooling demand and energy consumption we develop a reference building which is based on the IECC-Mexico 2016 and the NOM-020-ENER-2011. Per the client request we use Autoclaved Cellular Concrete blocks with 51mm Polystyrene insulation, double glazing and UPVC window framing. The reduced consumption from these measures was only 17% compared to the IECC reference. Thus, we implement in addition the use of instantaneous water heaters, LED interior and exterior lighting, daylight and presence sensors, EnergyStar home appliances, and outdoor air supply with heat recovery. Combining these approaches we reach savings of 52% in yearly energy consumption compared to the reference building. Finally, the software used permits the evaluation of photovoltaic system generation. This guided the change of the first floor roof angle center location to increase the south-oriented area in order to accommodate more solar panels. The change allows the number of solar panels to be double which was required to reach the net-zero threshold we were looking for. The roof change also opens a larger area in the north facade which benefits the natural ventilation performance. This would be discussed in a future article. Please share your opinion below, your participation means a lot to us.
* OWN, Architectural Firm with focus on balance between human and nature, www.thisisown.com/. ** sDA: Spatial Daylight Autonomy, measure defined in standard IES LM-83-2012. *** ASE: Annual Sunlight Exposure, measure defined in standard IES LM-83-2012.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Suggest topicsWeekly our team select the most relevant topic of the industry to talk about. However, our readers' interests are even better. Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|
GREEN BUILDING CERTIFICATION - ENERGY MODELING - |
Offices | OficinasCalle 20 438, Oficina 116,
Colonia México, Mérida, Yucatán, México 97125 +52 999 838-0096 [email protected] |
Copyright © 2018-2024 Chaac Simulaciones Inc. All Rights Reserved.
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed